STORMY WEATHER
Portal 4: Geography. Weather and climate
Vocabulary
WEATHER: the state of the atmosphere in a specific time and place.
CLIMATE: the most frequent state of the atmosphere in a specific place over a long period of time.
FRONT: area of contact between two masses of air. If the mass of cold rises over the hot air, a cold front is produced; if the opposite happens, a warm front is created.
GLACIERS: masses of aice that form when there is a continuous accumulation of snow high up in the mountains. They move slowly, occupy 10% of the Earth’s surface and hold 75% of the world’s fresh water, but global warming has caused some of them to recede and the loss of others.
The atmosphere

The atmosphere
Layers of the Atmosphere (Animation)
Weather and climate

Precipitation

3 Types of Rainfall
Climate change
Causes and Effects of Climate Change | National Geographic

THE CONTINENTS

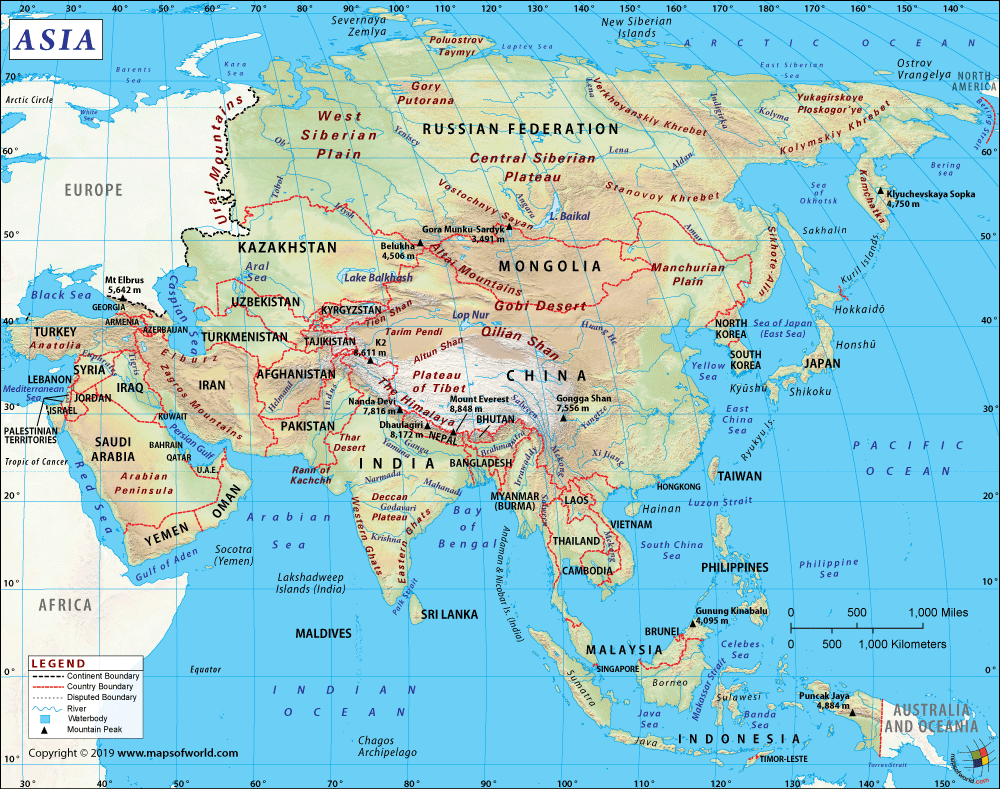

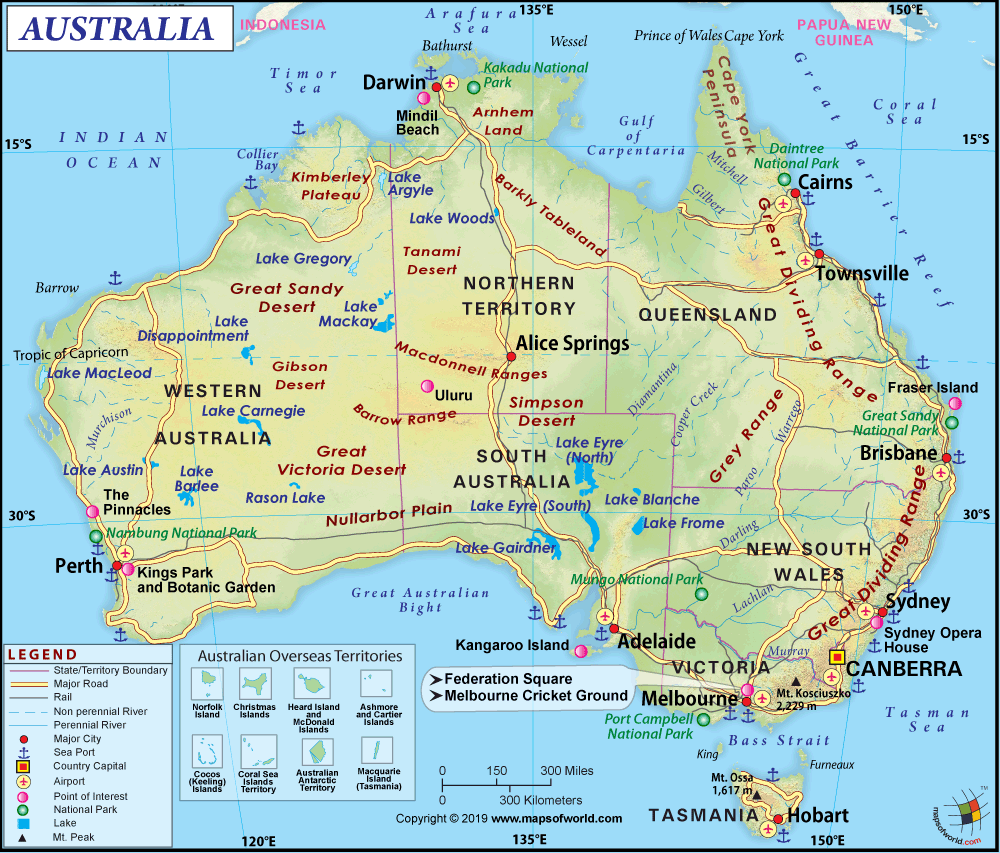
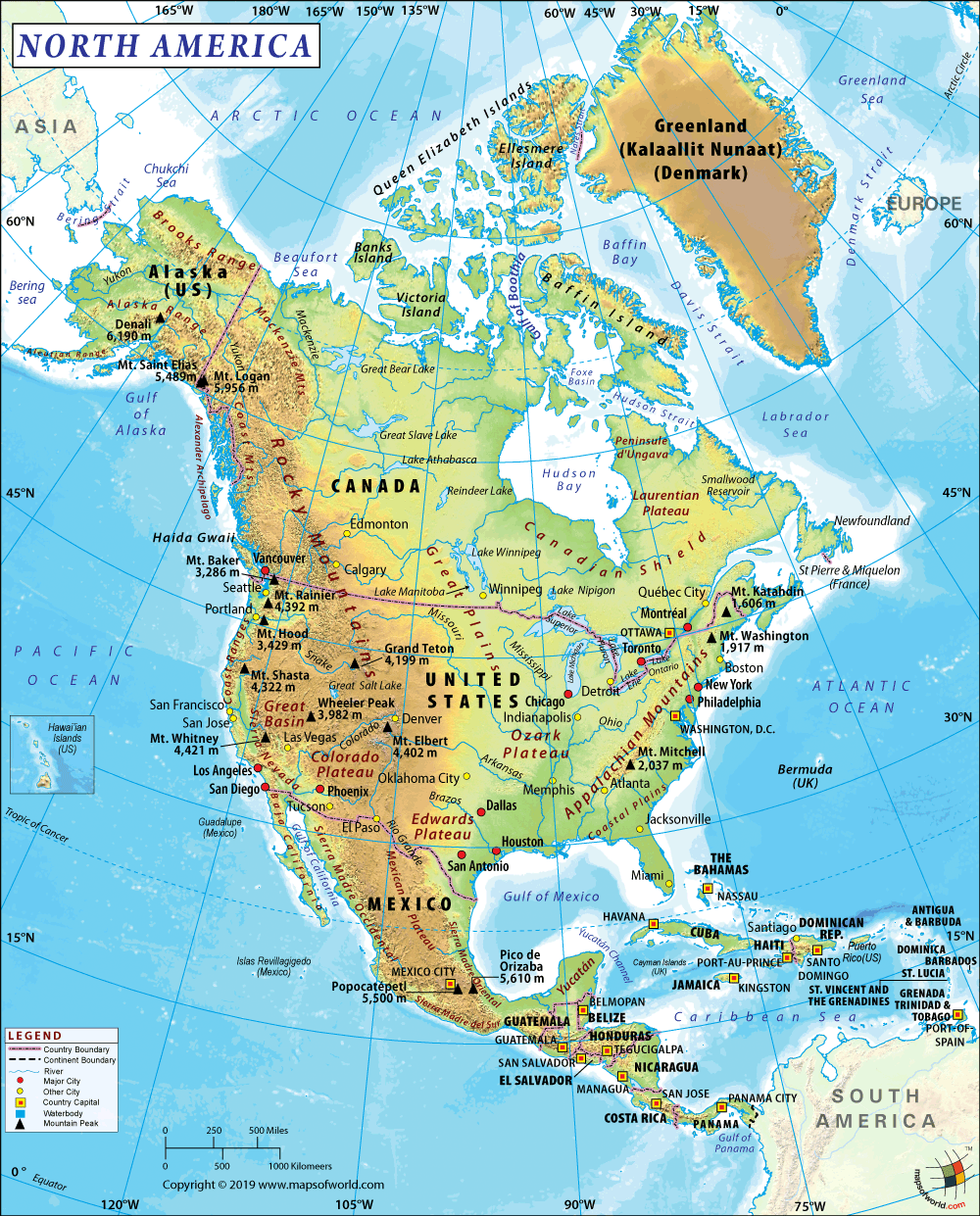


Do you want to play?


T H E C O N T I N E N T S
(Team Project)
-
FILE.
Name (Origin), Area, Population, Population density, G.P.D., G.P.D. per capita, H.D.I., Countries, Languages, Time zones, Largest cities.
2. LOCATION.
Natural borders, hemisphere, etc.
3. RELIEF.
Geology, plains, plateaus, massifs, mountain ranges, depressions, valleys, peninsulas, deserts.
4. CLIMATES AND LANDSCAPES.
Climates: Equatorial, Tropical, Desert, Oceanic, Continental, Temperate, Mediterranean,, Steppe, Polar.
Natural landscapes: temperatures, precipitation, soil, vegetation, fauna.
5. WATERS.
Rivers, lakes, glaciers, seas, oceans.
6. HUMANS AND ENVIRONMENT.
Changing landscapes:
- Types: rural, cultural, urban.
- Factors: land rotation, terraces, use of water, building infrastructures.
Pollution and overexploitation:
- Factors: population, energy, technology.
- Pollution: greenhouse effect, acid rain, sea pollution, growth of cities, infrastructures, development of tourist areas.
- Overexploitation: vegetation loss, soil erosion, drying of water tables, extinction of fauna.
- Society’s environmental measures: protective, preventive and corrective. Sustainable development.
